Nephrolithiasis and Uric Acid: Understanding Kidney Stones today
Nephrolithiasis and Uric Acid: Understanding Kidney Stones
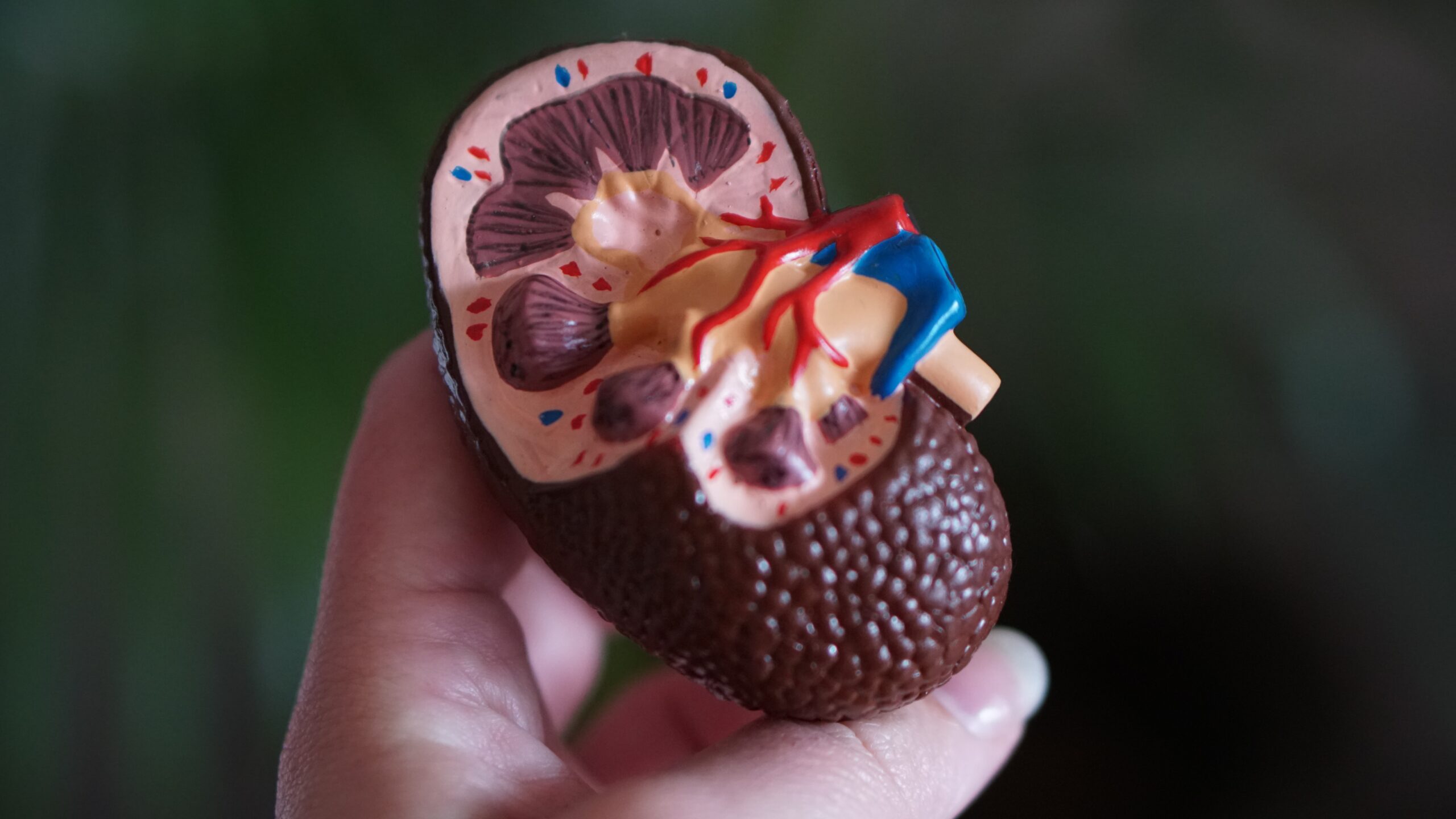
Nephrolithiasis, commonly known as kidney stones, affects a significant number of people worldwide. Among the different types of kidney stones, those composed of uric acid pose a unique challenge. In this brief article, we explore the relationship between nephrolithiasis and uric acid formation, shedding light on the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies.
Uric acid kidney stones form when there is an excessive amount of uric acid in the urine. Uric acid is a waste product that is normally excreted through urine, but in some cases, it can crystallize and accumulate in the kidneys, leading to stone formation. Several factors contribute to the development of uric acid kidney stones, including a diet high in purines (found in certain meats and seafood), dehydration, and certain medical conditions such as gout and metabolic disorders.
Symptoms of uric acid kidney stones often manifest as severe flank pain, blood in urine, frequent urination, and urinary tract infections. These stones can vary in size, ranging from tiny particles to larger, more obstructive stones. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to alleviate pain and prevent complications such as kidney damage or urinary tract obstruction.
Preventing uric acid kidney stones involves a multifaceted approach. Dietary modifications play a key role, including reducing the intake of purine-rich foods and maintaining adequate hydration to promote urine dilution and prevent crystal formation. Additionally, managing underlying conditions like gout and metabolic disorders is crucial to minimize the risk of stone recurrence.
Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and preventive strategies. Treatment options may include pain management, medication to reduce uric acid levels, and potentially, minimally invasive procedures to remove or break down larger stones.
In conclusion, nephrolithiasis and uric acid kidney stones present unique challenges to individuals affected by this condition. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies can help in managing and preventing the recurrence of these stones. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, seeking medical guidance, and adhering to prescribed treatment plans, individuals can work towards minimizing the impact of uric acid kidney stones on their quality of life.
(Note: This article provides a brief overview of the subject and does not substitute medical advice. If you suspect you may have kidney stones or require more information, consult with a healthcare professional.)



